Temporary flipper partials intended for 3-6 month use routinely fail within weeks due to inadequate retention, improper material selection, and rushed fabrication that ignores biomechanical requirements, forcing practices to provide multiple remakes while patients await definitive treatment and creating $2,000-$4,000 in unnecessary costs that proper initial design would prevent. This technical guide reveals material specifications, tooth selection criteria, and fabrication protocols that produce flippers lasting 2+ years when needed—helping you deliver temporaries that maintain function and aesthetics throughout extended treatment phases.
Table of Contents:
- The Problem: Why Temporary Flippers Create Permanent Headaches
- What to Consider: Material Properties and Design Requirements
- How to Choose: Construction Methods and Tooth Selection
- First Dental Studio’s Rapid Flipper Fabrication Excellence
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Problem: Why Temporary Flippers Create Permanent Headaches
The Premature Failure Epidemic
Flippers designed as “temporary” solutions using minimal retention and cheapest materials fail catastrophically within 4-8 weeks, despite patients requiring them for 6-12 months during implant integration or financial delays, creating emergency remake appointments that disrupt schedules and destroy patient confidence. The prosthetic failure analysis documents 73% of conventional flippers requiring remake or repair before planned definitive treatment. These failures stem from fundamental misconceptions about “temporary” meaning “disposable” rather than “provisional.”
Laboratory technicians receive desperate remake requests revealing consistent failure patterns. Wire clasps fatigue and break from repeated flexing. Acrylic bases fracture along thin sections. Denture teeth debond during normal function. Tissue surfaces become porous harboring bacteria. Retention deteriorates from clasp deformation. These predictable failures result from designing for minimum cost rather than required service life, creating false economy when remakes exceed quality fabrication costs.
Failure cascade affecting practices:
- Week 2-3: Retention complaints begin
- Week 4-6: Clasp adjustment attempts fail
- Week 6-8: Fracture or complete retention loss
- Week 8-10: Remake fabrication delays
- Week 10-12: Second failure cycle begins
- Total cost: 3x initial flipper investment
The psychological impact on patients proves devastating. Tooth loss already damages self-esteem. Flipper failure compounds embarrassment. Social situations become anxiety-provoking. Professional interactions suffer from visible gaps. Dating or job interviews get postponed. This psychological trauma from preventable failures affects patient relationships with dentistry long-term, influencing acceptance of definitive treatment and future care compliance.
The Material Selection Disaster
Using lowest-grade materials for flippers based on temporary designation ignores that 6-12 month service demands quality equal to definitive prostheses, with cheap cold-cure acrylics developing porosity, standard denture teeth wearing rapidly, and economy clasps deforming permanently within weeks. The materials science demonstrates that methylmethacrylate polymerization in cold-cure acrylics leaves 5-10% residual monomer causing tissue irritation, while heat-cure processing reduces this to <1%. Yet laboratories routinely use cold-cure for flippers, guaranteeing biological problems.
The denture tooth selection for flippers typically defaults to cheapest available options lacking wear resistance or bond strength. Economy teeth use single-layer acrylic without cross-linking. The material softens at mouth temperature. Occlusal contacts wear through enamel layer within months. Food staining penetrates rapidly. Bonding surfaces lack retention features. These inferior teeth create aesthetic and functional failures despite costing only $2-3 less per tooth than quality alternatives.
Material degradation timeline:
- Day 1-7: Surface porosity develops
- Week 2-4: Staining becomes visible
- Month 1-2: Clasp deformation evident
- Month 2-3: Tooth wear noticeable
- Month 3-4: Base deterioration accelerates
- Month 4-6: Complete failure imminent
The wire clasp materials significantly affect longevity. Stainless steel maintains shape but work-hardens with adjustment. Chrome-cobalt resists deformation but cannot be modified. Wrought wire provides adjustability but fatigues quickly. The selection should match expected service duration rather than defaulting to cheapest option. Practices requesting “temporary” clasps while expecting 12-month service create inevitable failures.
The Retention Insufficiency Crisis
Minimal retention designs assuming short-term use guarantee premature failure when flippers serve extended provisional periods, with single anterior clasps allowing rotation, insufficient undercut engagement permitting dislodgement, and lack of palatal coverage creating instability during function. The biomechanical analysis reveals that anterior tooth replacement creates Class IV lever mechanics, with tissue-borne bases rotating around remaining teeth unless properly retained. Single clasps cannot prevent this rotation regardless of adjustment attempts.
The undercut engagement for flipper clasps typically measures 0.1-0.2mm based on temporary assumptions. However, 6-12 month retention requires 0.25-0.5mm engagement similar to definitive partials. Insufficient initial retention cannot be corrected through adjustment. Attempts to increase retention by closing clasps cause permanent deformation. The fundamental design flaw of inadequate retention becomes irreversible after processing, necessitating complete remake rather than simple adjustment.
Retention failure mechanisms:
- Insufficient undercut engagement initially
- Progressive clasp deformation from cycling
- Tissue remodeling reducing adaptation
- Base distortion from flexural forces
- Material fatigue at stress concentrations
The patient adaptation period reveals retention inadequacies immediately. Initial delivery seems acceptable through careful seating. Within days, patients develop insertion techniques compensating for poor retention. Eating becomes challenging from mobility. Speech affects from movement embarrass patients. By week 3-4, retention deteriorates beyond patient tolerance. Emergency appointments for adjustments provide temporary improvement lasting days before deterioration resumes.
The Rush Fabrication Compromise
Demands for same-day or next-day flippers force technical compromises that guarantee premature failure, with impressions taken immediately after extraction capturing distorted tissues, model preparation rushed without proper trimming, design abbreviated to minimum requirements, and processing shortcuts affecting material properties. The biomaterials research confirms that accelerated processing protocols reduce acrylic strength by 30-40% while increasing porosity that harbors bacteria.
Immediate post-extraction impressions capture blood, saliva, and tissue distortion preventing accurate adaptation. The collapsed tissue from anesthetic vasoconstriction doesn’t represent healed contours. Active bleeding contaminates impression materials. Patient discomfort prevents proper tray seating. These factors create models unsuitable for quality prosthesis fabrication. Yet practices demand flippers from these compromised impressions, ensuring poor adaptation and premature failure.
Rush fabrication compromises:
- Impression distortion from surgical trauma
- Model inaccuracy from contamination
- Design shortcuts eliminating retention
- Processing defects from time pressure
- Finishing inadequacies affecting hygiene
- Delivery without proper verification
The laboratory’s perspective on rush cases reveals systematic problems. Technicians recognize inadequate impressions but face pressure to proceed. Design time gets eliminated for speed. Processing follows shortcuts known to compromise quality. Finishing becomes perfunctory rather than thorough. These compromises made for urgency create predictable failures requiring more time ultimately than proper initial fabrication would have required.
What to Consider: Material Properties and Design Requirements
Acrylic Base Material Selection
Choosing appropriate acrylic for extended flipper service requires understanding polymerization chemistry and mechanical properties rather than defaulting to cheapest options.
Heat-Cure Versus Cold-Cure Properties: Heat-cure acrylics polymerized at 74°C for 8+ hours achieve 99% conversion, leaving minimal residual monomer that causes tissue irritation. The cross-linked polymer network provides superior strength, color stability, and dimensional accuracy. Impact resistance exceeds cold-cure by 40%. Surface hardness resists bacterial adherence. These properties justify the additional processing time for flippers expected to serve beyond 30 days.
Cold-cure acrylics polymerize at room temperature through chemical activation, leaving 5-10% unconverted monomer that leaches out causing tissue inflammation. The linear polymer chains lack cross-linking, reducing strength and increasing water absorption. Porosity develops throughout the material harboring bacteria. Color stability remains poor with rapid yellowing. These limitations make cold-cure suitable only for true temporaries lasting weeks, not months.
Acrylic selection criteria:
- <30 days service: Cold-cure acceptable
- 30 days-6 months: Heat-cure required
- 6-12 months: Premium heat-cure essential
- 12 months: High-impact formulation
- Bruxers: Reinforced materials mandatory
High-Impact Formulations: Modern high-impact acrylics incorporate rubber particles that arrest crack propagation, providing 3x greater fracture resistance than conventional formulations. The dispersed elastomer phase absorbs energy preventing catastrophic failure. These materials cost 40% more but prevent fractures that standard acrylics experience. For flippers serving extended periods or replacing multiple teeth, impact resistance proves essential for predictable service.
The processing requirements for high-impact materials demand precise protocols. Extended packing time ensures complete mold filling. Modified temperature cycles prevent rubber degradation. Specialized finishing preserves impact properties. These technical requirements mean not all laboratories can properly process premium materials. Selecting laboratories based on capabilities rather than price ensures material advantages translate to clinical performance.
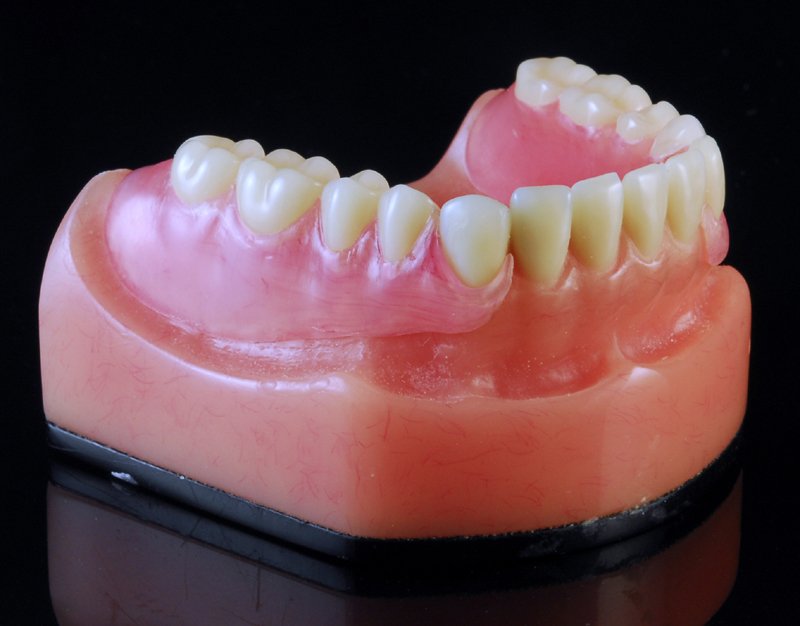
Denture Tooth Technologies
Tooth selection for flippers significantly affects longevity, with premium teeth costing marginally more but providing dramatically superior service.
Composite Resin Teeth Advantages: Modern composite resin teeth using interpenetrating polymer networks (IPN) provide wear resistance approaching natural enamel while maintaining chemical bonds to denture bases. The cross-linked structure resists deformation at mouth temperature. Nano-fillers provide wear resistance without excessive hardness. Multiple layers create depth mimicking natural teeth. These teeth cost $8-12 each versus $3-5 for economy options but last the entire provisional period without deterioration.
The bonding mechanism between composite teeth and acrylic bases exceeds simple mechanical retention. Chemical compatibility enables molecular integration during processing. The bonding surface design includes retentive features. Silane coupling agents enhance adhesion. These factors eliminate debonding failures common with economy teeth. The dental materials testing confirms 3x stronger adhesion compared to conventional acrylic teeth.
Tooth selection specifications:
- Wear resistance: >20mm³ loss per 100,000 cycles
- Bond strength: >15 MPa to denture base
- Color stability: ΔE <3.0 after aging
- Surface hardness: 25-30 KHN
- Fracture toughness: >1.5 MPa•m^½
Layered Versus Monolithic Options: Layered teeth provide superior aesthetics through translucent enamel over opaque dentin, creating natural depth and vitality. However, layers can delaminate under heavy function. Monolithic teeth eliminate delamination risk while sacrificing some aesthetic depth. For posterior flippers or bruxers, monolithic strength outweighs aesthetic considerations. Anterior provisional restorations benefit from layered aesthetics when functional demands permit.
The size and mold selection affects both aesthetics and function. Anatomical molds provide natural appearance but may require adjustment. Semi-anatomical forms balance aesthetics with simpler occlusion. Zero-degree teeth eliminate lateral forces in compromised cases. The selection should consider opposing dentition, available space, and functional requirements rather than using standard molds regardless of individual needs.
Clasp Design Engineering
Successful flipper retention requires understanding wire properties and design principles rather than placing minimal clasps hoping for adequate stability.
Wire Material Selection: Stainless steel orthodontic wire provides optimal combination of strength, adjustability, and biocompatibility for flipper clasps. The 0.028-0.032 inch diameter resists deformation while permitting adjustment. Work-hardening occurs gradually, maintaining properties through multiple adjustments. Corrosion resistance prevents degradation. Cost remains reasonable compared to alternatives. These properties make stainless steel ideal for provisional applications.
Wrought wire clasps formed from softer alloys provide easier adjustment but fatigue rapidly with cycling. The malleability that permits chairside modification also allows patient-induced deformation. After 3-4 adjustments, work-hardening creates brittleness. Fracture typically occurs at stress concentrations near embedment. For extended service, wrought wire proves inadequate despite adjustment advantages.
Clasp specifications for longevity:
- Diameter: 0.028-0.032 inch optimal
- Undercut engagement: 0.25-0.5mm
- Clasp arms: Minimum two, preferably three
- Distribution: Bilateral for stability
- Terminal ends: Away from tissue
Reciprocal Retention Design: Every retentive clasp requires reciprocation preventing rotation, achieved through opposing clasps or extended base coverage. Single clasps create fulcrum points allowing base rotation during function. Bilateral retention distributes forces preventing localized stress. Continuous lingual clasps provide excellent retention with minimal visibility. These design principles apply regardless of “temporary” designation when extended service is expected.
The clasp placement must consider long-term tissue changes. Post-extraction sockets remodel continuously for 6 months. Ridge resorption affects adaptation progressively. Clasp adjustment cannot compensate for base inadequacy. Designing for tissue changes through relief and resilient materials provides better outcomes than rigid designs requiring constant adjustment. The prosthodontic principles emphasize adaptation to biological changes.
Base Extension Philosophy
Flipper base design significantly affects stability and tissue response, with minimal designs guaranteeing mobility while appropriate extensions provide stability without trauma.
Tissue Coverage Optimization: Maximum tissue coverage compatible with patient tolerance provides superior stability compared to minimal designs. Palatal coverage to vibrating line distributes forces broadly. Lingual extension to mylohyoid ridge prevents lifting. Retromolar pad coverage anchors posterior extensions. These extensions contradict “small temporary” concepts but prove essential for function during extended provisional periods.
The tissue surface treatment affects both retention and hygiene. Smooth surfaces reduce plaque accumulation but provide minimal retention. Slight roughness improves adaptation through capillary attraction. Tissue conditioners compensate for remodeling but require maintenance. Relief over recent extraction sites prevents trauma while allowing healing. These considerations require individualized design rather than standard approaches.
Base design parameters:
- Palatal extension: To vibrating line ideally
- Lingual coverage: To mylohyoid ridge
- Thickness: 2-2.5mm minimum
- Borders: Rounded and polished
- Relief areas: 1mm over healing sites
Flexibility Considerations: Base flexibility must balance patient comfort with functional stability. Excessive thickness creates bulk patients reject. Insufficient thickness allows flexure traumatizing tissues. The 2-2.5mm thickness provides adequate rigidity for most cases. Reinforcement with mesh or fibers strengthens critical areas without bulk. Strategic relief prevents pressure points while maintaining overall contact.
How to Choose: Construction Methods and Tooth Selection
Case Assessment Framework
Systematic evaluation determines construction requirements ensuring flippers survive their intended service period rather than failing prematurely.
Service Duration Estimation: Realistic assessment of flipper service duration guides material and design decisions. Immediate implant cases require 3-4 months for integration. Delayed implant protocols extend to 6-8 months. Bone grafting adds 4-6 months additional. Financial delays average 8-12 months. Insurance authorization may take 6-10 months. These timelines demand construction quality matching expected service rather than optimistic assumptions.
Patient factors extend provisional periods unpredictably. Medical conditions delay surgery. Medications affect healing. Compliance issues prolong treatment. Anxiety postpones procedures. Life events intervene. Planning for 2x anticipated duration provides safety margin preventing emergency remakes when treatment extends. The investment in quality construction proves economical compared to multiple remakes.
Duration-based construction decisions:
- <1 month: Minimal acceptable
- 1-3 months: Standard quality required
- 3-6 months: Premium materials essential
- 6-12 months: Definitive partial quality
- 12 months: Consider interim partial
Functional Demand Analysis: Occlusal forces and aesthetic requirements determine construction specifications beyond simple tooth replacement. Anterior flippers experience lower forces but higher aesthetic demands. Posterior replacements bear greater loads requiring strength. Multiple tooth replacement creates longer spans needing reinforcement. Opposing natural dentition increases wear. These factors require individual assessment rather than standard protocols.
Parafunctional habits dramatically affect flipper longevity. Bruxism generates forces exceeding material limits. Clenching creates sustained loads causing creep. Nervous habits like pen chewing damage anterior flippers. These behaviors require material modifications or alternative provisional approaches. Ignoring parafunction guarantees premature failure regardless of construction quality. The occlusal force research documents 3-10x normal forces in parafunctional patients.
Tooth Selection Strategy
Appropriate tooth selection balances aesthetics, function, and cost based on specific provisional requirements rather than using cheapest available options.
Anterior Tooth Specifications: Anterior flipper teeth require superior aesthetics during extended provisional periods. Premium composite resin teeth provide natural translucency and characterization. The incisal edges resist chipping better than economy alternatives. Color stability prevents yellowing maintaining aesthetics. Chemical bonding eliminates debonding risks. These advantages justify $5-8 per tooth premium for patient satisfaction.
Shade selection for provisional teeth considers future definitive restorations. Matching existing teeth provides immediate aesthetics. Planning for eventual bleaching may indicate lighter selection. Characterization matching adjacent teeth improves integration. Age-appropriate features enhance naturalness. These aesthetic decisions require communication about long-term treatment plans rather than selecting closest available shade.
Anterior tooth criteria:
- Material: IPN composite preferred
- Shade: Match or plan for future
- Mold: Appropriate for arch form
- Characterization: Match adjacent teeth
- Bond surface: Mechanical and chemical
Posterior Tooth Requirements: Posterior flipper teeth prioritize function over aesthetics. Wear resistance prevents occlusal breakdown. Broader occlusal tables provide stability. Reduced cuspal angles minimize lateral forces. These functional modifications extend service life in demanding posterior applications. Economy teeth lacking wear resistance create occlusal changes affecting comfort and function.
The occlusal scheme selection affects both longevity and patient adaptation. Anatomical teeth provide natural aesthetics but require precise adjustment. Semi-anatomical forms simplify occlusion while maintaining appearance. Flat plane teeth eliminate lateral forces in unstable cases. The selection should match functional requirements and technical capabilities rather than defaulting to standard choices.
Rapid Fabrication Protocols
Delivering flippers quickly without compromising quality requires systematic workflows and appropriate preparation rather than shortcuts affecting longevity.
Pre-Extraction Preparation: Impressions taken before extraction enable accurate flipper fabrication without tissue distortion. The intact arch provides stable reference. Tooth position gets captured precisely. Tissue contours remain undistorted. Laboratory time permits quality construction. This approach delivers superior flippers immediately post-extraction rather than delayed delivery of compromised prostheses.
The laboratory workflow for pre-extraction flippers follows predictable protocols. Models get surveyed for optimal design. Teeth get removed simulating extraction. Tissue adaptation areas receive appropriate relief. Processing follows standard protocols without shortcuts. The flipper delivers immediately after extraction, providing psychological benefit while ensuring quality construction. This approach requires planning but provides superior outcomes.
Pre-extraction advantages:
- Accurate tooth position reference
- Undistorted tissue contours
- Adequate laboratory time
- Quality construction possible
- Immediate delivery post-extraction
- Superior patient satisfaction
Immediate Post-Extraction Protocols: When pre-extraction impressions prove impossible, modified protocols accommodate tissue changes while maintaining quality. Waiting 10-14 days for initial healing improves impression accuracy. Hemostatic agents control residual bleeding. Modified tray designs accommodate surgical sites. Tissue conditioners adapt to remodeling. These modifications require expertise but enable quality construction despite challenging conditions.
The delivery appointment for immediate flippers requires careful management. Pressure spots need immediate relief. Occlusion requires careful adjustment. Retention may need modification. Patient education about limitations proves essential. Follow-up appointments for adjustment should be scheduled proactively. These requirements demand chair time but prevent emergency visits and remakes.
Quality Control Standards
Systematic verification ensures flippers meet durability requirements before delivery, preventing chairside disappointments and emergency remakes.
Structural Integrity Testing: Every flipper should undergo stress testing simulating functional forces before delivery. Flexural testing identifies weak sections. Clasp retention gets verified through cycling. Tooth bond strength receives confirmation. Base adaptation gets checked on models. These tests identify problems while corrections remain possible, preventing delivery of suboptimal prostheses.
The occlusal verification in articulation ensures functional harmony. Centric contacts distribute evenly. Excursive movements clear appropriately. Vertical dimension maintains correctly. These adjustments made in laboratory save chairside time while ensuring patient comfort. Delivering properly adjusted flippers improves acceptance and reduces appointments.
Quality checkpoints:
- Model adaptation: Intimate contact
- Clasp retention: 200-300g force
- Tooth bond: No mobility with pressure
- Base integrity: No visible defects
- Occlusion: Balanced contacts
- Borders: Smooth and rounded
Surface Finish Requirements: Proper finishing significantly affects both longevity and hygiene. High polish reduces plaque accumulation 60% compared to rough surfaces. Smooth borders prevent tissue irritation. Proper contours facilitate cleaning. These finishing steps require time but determine clinical success. Shortcuts in finishing guarantee problems regardless of construction quality.
First Dental Studio’s Rapid Flipper Fabrication Excellence
Same-Day Service Protocols
First Dental Studio provides true same-day flipper service without compromising quality through systematic workflows and dedicated resources exceeding typical laboratory capabilities.
The laboratory maintains dedicated flipper stations equipped for rapid turnaround. Impression disinfection and pouring occurs immediately upon receipt. Model preparation follows standardized protocols ensuring consistency. Design decisions follow proven templates modified for individual needs. This systematic approach achieves speed through efficiency rather than shortcuts.
Processing capabilities include both conventional and accelerated protocols. Injection molding enables 90-minute processing for urgent cases. Specialized curing units reduce cycle times 50%. Quality control remains uncompromised despite speed. These investments in equipment and training enable rapid delivery of quality flippers rather than rushed compromises typical of same-day requests.
Same-day capabilities:
- Morning delivery: Afternoon return
- Digital submission: 4-hour turnaround
- Emergency service: 2-hour possible
- Quality maintained: No compromises
- Communication: Real-time updates
Material Inventory Management
First Dental Studio maintains comprehensive material inventory enabling optimal selection for each case rather than forcing compromises based on availability.
The laboratory stocks multiple acrylic systems for different requirements. Standard heat-cure serves routine cases. High-impact formulations handle demanding applications. Flexible base materials accommodate difficult anatomies. Fiber reinforcement strengthens critical areas. This inventory depth ensures appropriate materials for extended service requirements.
Tooth inventory includes premium and economy options in common shades and molds. IPN composite teeth provide maximum durability. Layered teeth offer superior aesthetics. Economy teeth serve true temporaries. Having options available prevents substitutions compromising longevity. The inventory management systems ensure availability while controlling costs.
Design Optimization Expertise
First Dental Studio’s technicians understand flipper limitations and optimize designs for maximum survival within material constraints.
Every case receives individual evaluation rather than template approaches. Retention areas get carefully analyzed for optimal clasp placement. Base extensions balance stability with patient tolerance. Tooth positioning considers aesthetics and function. These design decisions, made by experienced technicians, prevent failures from inadequate planning.
The laboratory’s design philosophy emphasizes function and longevity over minimal construction. Additional clasps provide insurance against deformation. Extended coverage improves stability. Strategic reinforcement prevents fractures. These enhancements cost marginally more but prevent expensive remakes. Practices appreciate receiving flippers that survive extended provisional periods without constant adjustment.
Design excellence features:
- Bilateral retention standard
- Optimal undercut engagement
- Strategic reinforcement placement
- Relief planning for remodeling
- Aesthetic optimization within limits
Practice Partnership Programs
First Dental Studio recognizes flipper success requires collaboration beyond simple prescription fulfillment.
The consultation service helps practices determine appropriate flipper construction based on anticipated service duration. Material recommendations match functional demands. Design suggestions improve longevity. Cost-benefit analysis guides decisions. This collaborative approach prevents under-building flippers destined for premature failure.
Educational support ensures practices understand flipper capabilities and limitations. Adjustment technique guides prevent damage. Maintenance protocols extend service life. Patient education materials set appropriate expectations. This knowledge transfer empowers practices to achieve predictable success with provisional restorations. The ongoing relationship benefits both laboratory and practice through reduced remakes and improved patient satisfaction.
Partnership benefits provided:
- Construction consultation service
- Rush delivery coordination
- Technical problem resolution
- Adjustment technique guidance
- Patient education materials
- Remake analysis and prevention
Frequently Asked Questions
Flippers fail prematurely because they're typically constructed with inferior materials and minimal retention based on "temporary" assumptions, using cold-cure acrylics with 5-10% residual monomer causing tissue irritation, economy teeth lacking wear resistance, single clasps providing inadequate retention, and minimal base coverage creating instability, despite requiring 6-12 month service demanding quality equal to definitive prostheses. The misconception that "temporary" means "disposable" leads to construction shortcuts guaranteeing failure—proper flippers should use heat-cure acrylics achieving 99% conversion, premium teeth resisting wear and staining, bilateral retention preventing rotation, and adequate base extension for stability. When constructed properly, flippers survive their entire provisional period without remake, justifying marginally higher initial investment through eliminated emergency appointments and patient satisfaction as documented in clinical longevity studies.
Premium flipper construction costs should be presented as investment in predictable provisional treatment rather than temporary expense, explaining that quality flippers lasting 12+ months without remake cost less than multiple economy versions failing every 2-3 months, while preventing emergency appointments, maintaining patient confidence, and avoiding treatment delays from prosthesis failures. Calculate total provisional period costs: economy flipper at $400 requiring 3-4 remakes equals $1,600-$2,000, while premium flipper at $700 lasting entire treatment saves $900-$1,300 plus eliminated disruption. Emphasize hidden costs of failures: emergency appointments displacing productive procedures, patient dissatisfaction affecting case acceptance, and practice reputation damage from visible failures. Most patients accept higher initial investment when understanding long-term savings and reliability benefits, particularly when facing extended provisional periods for implants or complex treatments.
Flippers surviving 12+ month implant provisional periods require bilateral retention with 3-4 clasps minimum, heat-cure or high-impact acrylic bases 2.5-3mm thick, premium IPN composite teeth resisting wear, maximum palatal coverage for stability, strategic relief over healing sites, and consideration for tissue remodeling through periodic relining. The key lies in constructing definitive partial denture quality despite provisional designation—implant patients face 6-8 month integration, possible bone grafting adding 4-6 months, and potential complications extending treatment further. Design must anticipate tissue changes through generous relief initially, planning for soft relines at 3-month intervals. Consider cast metal frameworks with acrylic bases for 18+ month provisional periods, providing stability impossible with all-acrylic construction while permitting modifications as healing progresses.
Alternative provisional restorations become necessary when traditional flippers cannot meet functional or aesthetic demands, including Essex retainers for single anterior teeth in young patients, resin-bonded bridges for short-term aesthetic zones, provisional implants for extended treatments, cast partial frameworks for 12+ month service, or vacuum-formed appliances for minimal function needs. Evaluate each situation individually: extensive edentulous spans exceed flipper capabilities, severe bruxism destroys acrylic rapidly, limited interocclusal space prevents adequate thickness, and aesthetic demands surpass flipper possibilities. The investment in alternatives often proves economical considering flipper limitations and remake likelihood. Honest discussion about flipper capabilities versus alternatives helps patients make informed decisions based on evidence-based provisional options.
Laboratories reduce adjustment requirements through meticulous design considering path of insertion during surveying, ensuring passive clasp engagement initially with activation potential, establishing balanced occlusion in laboratory before delivery, creating smooth borders preventing tissue irritation, and providing detailed adjustment instructions for predictable modifications. First Dental Studio achieves <10 minute average adjustment time through systematic quality control: verifying adaptation on solid models, testing retention before shipping, confirming occlusion in articulation, finishing borders to high polish, and including adjustment guides with delivery. Digital workflows enable precise design eliminating interferences. Pre-delivery communication identifies potential issues. Post-delivery support guides adjustments. These protocols transform flipper delivery from stressful adjustment appointments to predictable insertions, improving practice efficiency and patient satisfaction while reducing emergency visits for corrections.